Experimental



















Integrated Proton Transfer Reaction Mass Spectrometer ( PTR-MS ) for Advancements in Atmospheric Chemistry and Aerosol Science by providing Long-Term, High-Resolution Chemical Characterization of Ambient Air in Urban High-Altitude Sites.






Measures the number size distribution of aerosols from 5-1000 nm in high time and size resolutions in online and realtime mode.






An aerosol chemical speciation monitor which can be ued for chemical characterization of atmospheric aerosols






Measures mass variation per unit area by measuring changes in resonant frequency of a quartz crystal.






PCR Thermocycler can be used for the characterization of biodiversity, cloning, medical applications like gene therapy, cancer therapy etc.












Spectroradiometer Based Laboratory Measurement of Aerosol Absorbance Spectra






Calibration setup for low cost sensors and indoor air research laboratory.






Cross Photolysis Cavity Ring Down Spectrometer, GC-IR and GC-MS






Measures the number size distribution of aerosols from 5-1000 nm in high time and size resolutions in online and realtime mode.






Measures the number of aerosols capable of forming cloud condensation nuclei in the atmosphere under different prevailing supersaturations.






Experimental facility for Stack Emissions Measurements and Evaluation of Air Pollution Control Equipment






Motorized advanced fluorescence microscope for BF and Fluorescence imaging to study bio-aerosols, microorganisms, microplastics, etc.






10-stage cascade impactor for size-resolved sampling of particles






Low cost mobile air quality monitoring






Ambient air quality monitoring station at IIT Madras and data assessment






Pulsed Laser Photolysis-Laser Induced Fluorescence spectrometer.






Aethalometer calculates the instantaneous concentration of optically absorbing aerosols from the rate of change of the attenuation of light transmitted through the particle-laden filter.





Modeling
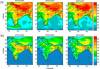


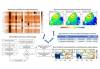

Monthly (April) average surface ozone calculated for (a)24 h and (b) noontime (11:30–16:30 IST). The average ozone mixing ratios (ppbv) from observations are also shown for comparison on the same colour scale. Note the difference in colour scales in the top and bottom rows.
Description of work : Wrf-chem was a regional atmospheric chemistry model used to simulate ozone and trace gases.
Works /publications : WRF-Chem simulated surface ozone over south Asia during the pre-monsoon: effects of emission inventories and chemical mechanisms






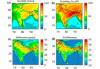
(a) Total Wheat production (Rabi growing season) in tonnes/model grid; (b) Percentage relative yield loss (%RYL); and (c) Crop production loss (CPL) for wheat in tonnes/model grid in each model grid.
Description of work :Wrf-chem was a regional atmospheric chemistry model used to simulate ozone and trace gases.
Works /publications : Revisiting the crop yield loss in India attributable to ozone






Distribution of simulated mean surface ozone (ppbv) (a) in reference simulation WRF-Chem, (b) in ddep_O3_off simulation; (c) difference between (b,a); (d) percentage difference between (b,a) with respect to (b) for April 2013.
Description of work :Wrf-chem was a regional atmospheric chemistry model used to simulate ozone and trace gases.
Works /publications : Effects of Dry Deposition on Surface Ozone over South Asia Inferred from a Regional Chemical Transport Model






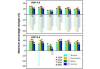
Seasonal variation of Hg wet deposition from 2013-2016*
Description of work : GEOS-chem was a global atmospheric chemistry model used by the research groups worldwide to simulate oxidant-aerosol system
Works /publications : Modelling of atmospheric mercury in India






Maximum percent change in projected seasonal mean of biomass burning during 2020-2100 releative to 2010 over 6 regions under RCP4.5 and RCP8.5.*
Description of work : GEOS-chem was a global atmospheric chemistry model used by the research groups worldwide to simulate oxidant-aerosol system
Works /publications : seasonal variation of AOD under RCP scenarios over India: Implication of biomass burning






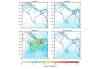
(a) Total7-days of back trajectory (at different heights) analyses in different transects during the sample collecting period.
Description of work : Box models and receptor models like HYSPLIT/STILT were used






(a) Total7-days of back trajectory (at different heights) analyses in different transects during the sample collecting period.
Description of work : Box models and receptor models like HYSPLIT/STILT were used






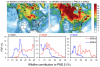
Projected increases in wildfires may challenge regulatory curtailment of PM2.5 over the eastern US by 2050
Abstract
The anthropogenic contribution to fine particulate matter (PM2.5) concentrations has sharply declined in North America, but there has been a concerning increase in air pollution events caused by wildfires due to recent warming. Based on model simulations, we project that summertime wildfire-induced PM2.5 concentrations in North America will almost double by the mid-21st century compared to present levels.





Laboratory








NABHA Laboratory is a collaboration between IIT Madras and College of Engineering, Munnar. The first of its kind lab in India is located in Munnar, Kerala, on an elevation of approximately 1600m above MSL. The lab focuses on studying ambient aerosol properties to understand the climate change scenario in South India. Its strategic location away from dense urban agglomeration and roadsides with low-level monsoon clouds passing very close to the surface makes it ideal for investigating natural atmospheric conditions. The lab aims to better understand aerosol-cloud-precipitation-climate interactions critical to understanding the impact of pollution on climate change. The data gathered from this lab shall be used in pollution-related policy making, climate change studies, understanding precipitation events in the monsoon period, and studying the origin and effects of bio-aerosols.
